Articles
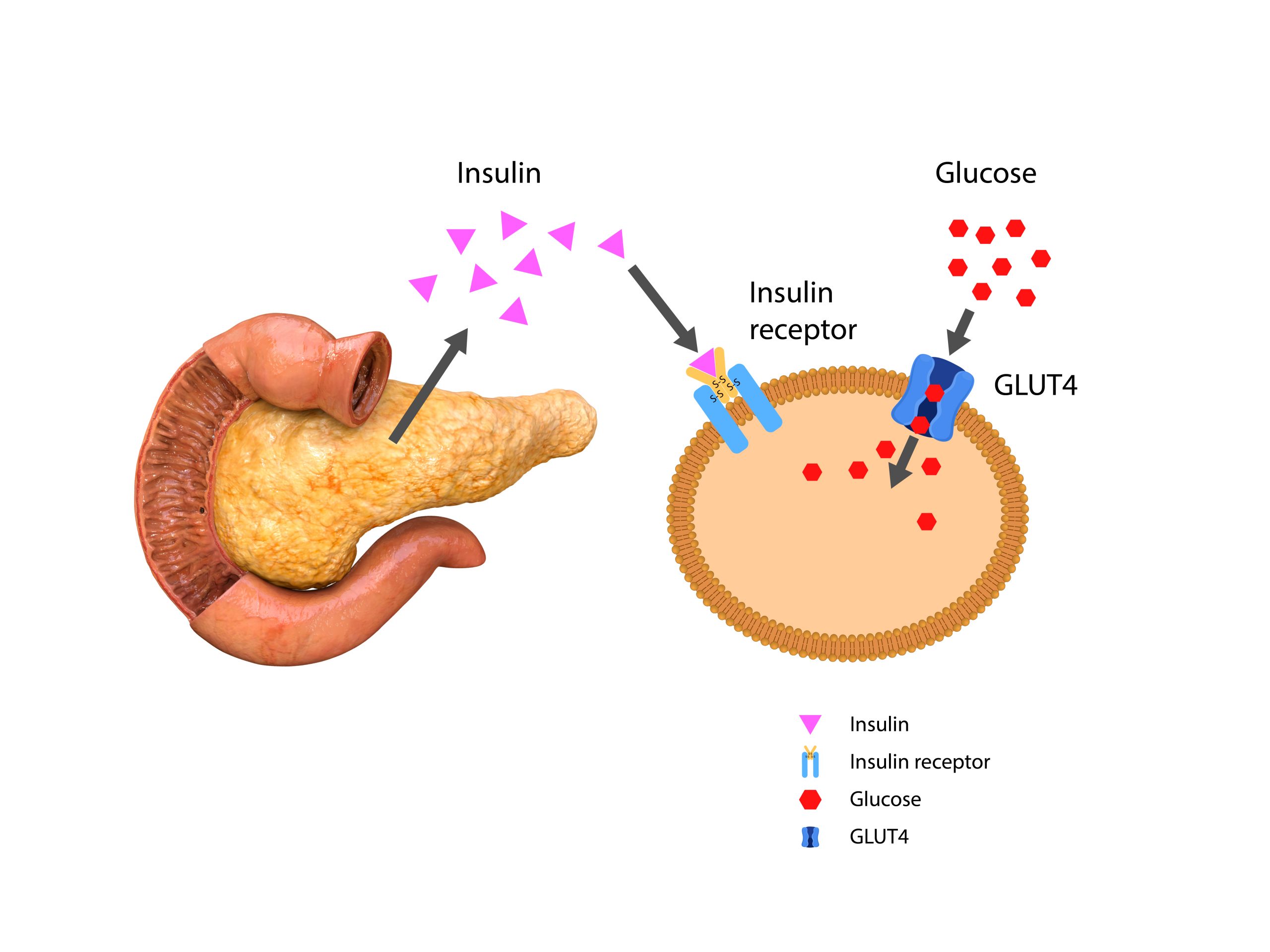
Insulin Resistance
What is Insulin?
Insulin is a vital hormone produced by the pancreas. Its main functions include:
- Keeping blood glucose levels normal.
- Playing a role in breaking down and storing fats and proteins.
Difference Between Insulin Resistance and Type 2 Diabetes
| Insulin Resistance | Type 2 Diabetes |
|---|---|
| The pancreas produces enough insulin, but cells are less responsive to it. | The pancreas does not produce enough insulin, but cells respond to it. |
What is Insulin Resistance?
Insulin resistance is a condition where cells respond poorly to insulin, causing the pancreas to produce more insulin to keep blood glucose levels normal. This leads to a state known as hyperinsulinemia.
Diagnosing Insulin Resistance
A common test for diagnosing insulin resistance is HOMA-IR, which combines fasting glucose and insulin results in a formula:
HOMA-IR Formula:
Test Results Interpretation
| Interpretation | Normal | Beginning of Insulin Resistance | Insulin Resistant |
|---|---|---|---|
| HOMA-IR Value | 0.5 - 1.4 | >1.9 | >2.9 |
Risk Factors for Insulin Resistance
Most at-risk individuals include:
- Overweight individuals.
- People following high-calorie, high-carb diets.
- Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS).
- Individuals with Cushing's Disease.
Other Causes
- Fat accumulation around the pancreas and cells.
- High insulin levels in the blood.
- Elevated inflammation levels.
- Genetic predisposition.
Symptoms of Insulin Resistance*
- Fatigue
- Hunger
- Difficulty concentrating
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol levels
- Weight gain (especially around the abdomen)
*These symptoms typically appear as insulin resistance progresses.
Effects of Untreated Insulin Resistance
If left untreated, insulin resistance can lead to:
- Type 2 diabetes
- Heart disease
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
Treating Insulin Resistance
The most effective way to treat insulin resistance is by adopting a healthy, active lifestyle, which includes:
- A balanced, nutritious diet or weight-loss plan if overweight.
- A personalized exercise program.
- Quitting smoking.
- Reducing sugar intake.
- Managing stress.
- Getting adequate sleep.
Diet Tips for a Balanced Diet
- A low-to-moderate glycemic index (GI) diet is often recommended.
- Consume 4-5 servings of vegetables and 2-3 servings of fruits daily.
- Minimize fast food intake.
- Reduce foods high in saturated fats and hydrogenated oils.
Tips to Increase Physical Activity
- Use stairs instead of elevators.
- Park farther away to increase walking distance.
- Engage in family or friend activities like biking, soccer, or basketball.
Glycemic Index Classification
It’s best to consume foods with low or moderate GI as they have a minimal impact on blood sugar levels. High GI foods can be eaten occasionally.
| Low GI Foods (≤55) | Moderate GI Foods (56-69) | High GI Foods (≥70) |
|---|---|---|
| Quinoa | Couscous | White bread |
| Pasta | Apricots | Bagels |
| Milk | Rye bread | Potatoes (fried, mashed) |
| Oats | Pineapple | Watermelon |
| Oranges | Ice cream | Breakfast cereal (without added sugar or fruits) |
| Bulgur | Grapes | Honey |
| Bran bread | Brown rice | Soft drinks |
| Lentils | Raisins | Instant rice and pasta |
| Boiled sweet potatoes | Beets | Parsnips |
| Cooked beans | Oat cakes | - |
| Banana | - | - |
| Blueberries | - | - |
| Pear | - | - |
| Peach | - | - |
| Orange | - | - |
| Mango | - | - |
References:
